Vertex Bridge - Software Integration
Introduction
Vertex Bridge offers multiple connectivity options. In this section we explain how to use these to communicate with a connected add-on (e.g. additional sensor).
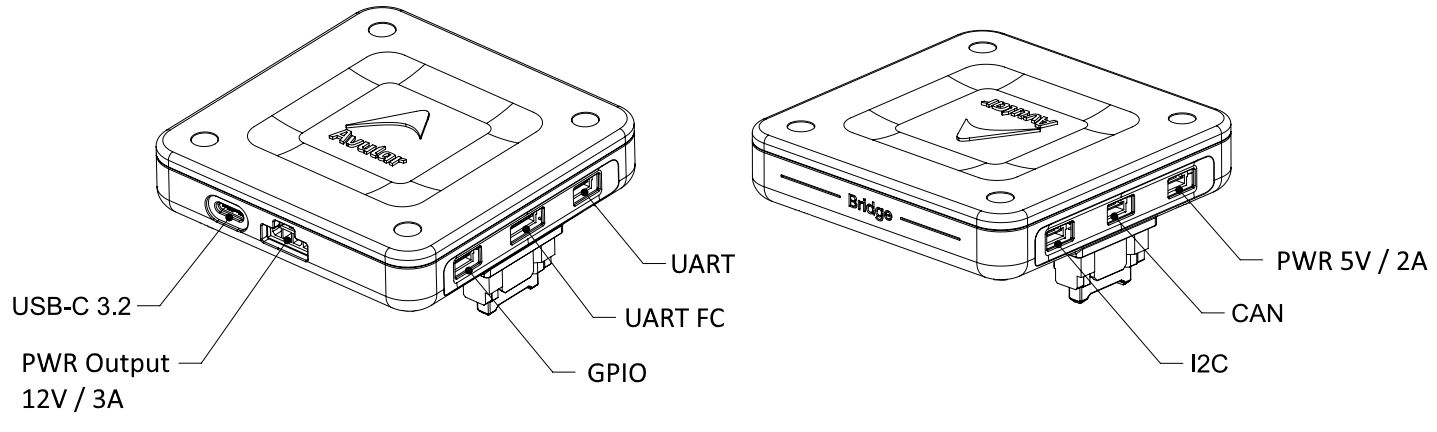
Connectivity Overview (External)
Connectivity Overview (Internal)
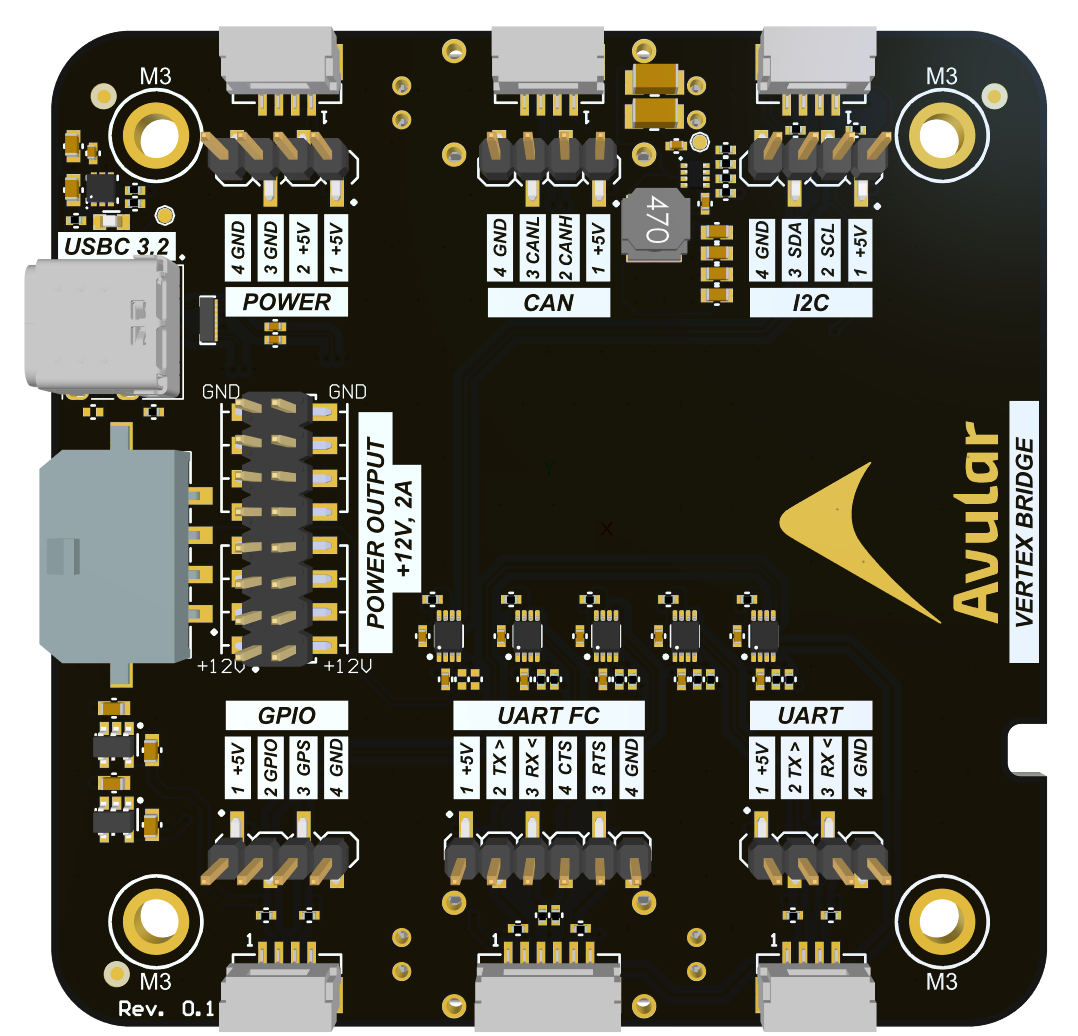
GPIO Connector
GNSS Pin
The GNSS module in the Vertex One outputs a synchronised timepulse on the GNSS pin. This timepulse is always active. Once a GNSS fix is available, it will be synchronised with GNSS.
GPIO Pin
The GPIO pin on the Bridge is Jetson GPIO07. See below a Python example code can be used to drive the pin:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# Pin Definitions
output_pin = 12 # BCM pin 18, BOARD pin 12
def main():
# Pin Setup:
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # BCM pin-numbering scheme from Raspberry Pi
# set pin as an output pin with optional initial state of HIGH
GPIO.setup(output_pin, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.HIGH)
print("Starting demo now! Press CTRL+C to exit")
curr_value = GPIO.HIGH
try:
while True:
time.sleep(1)
# Toggle the output every second
print("Outputting {} to pin {}".format(curr_value, output_pin))
GPIO.output(output_pin, curr_value)
curr_value ^= GPIO.HIGH
finally:
GPIO.cleanup()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
UART FC Connector
To send messages to this UART use /dev/serial-top
UART Connector
This UART port is by default the Debug port of the Jetson. This will show the debug output and eventually opens a shell for the user. See this video on how to use it:
How to use Jetson Debug port (External Link)
I2C Connector
The I2C port is connected to bus 8. Some examples of how to use the I2C port are:
To test if your I2C device is properly connected execute i2cdetect -y 8. If it shows the address of your device then the connection is working.
CAN Connector
To use the CAN bus the python-can is an easy to use library. More info here:
USB-C 3.2 Connector
The USB-C connector allowed you to connect a peripheral to the Vertex One through the USB 10 Gbit/s interface